Convert PFX Certificate
While having your SSL/TLS certificate in a PFX file is great, as most applications support the PFX file, there are still some cases where a PFX file is not supported, and you need the certificate in the PEM format as a CRT file (also called a CER file) with a key file (also called a PEM file).
In this post, I will show you step-by-step how to convert a PFX file into a single file or individual files with and without passwords each method supports the PEM format.
Prerequisites
- OpenSSL binary installed. You can find the OpenSSL binaries on the OpenSSL wiki.
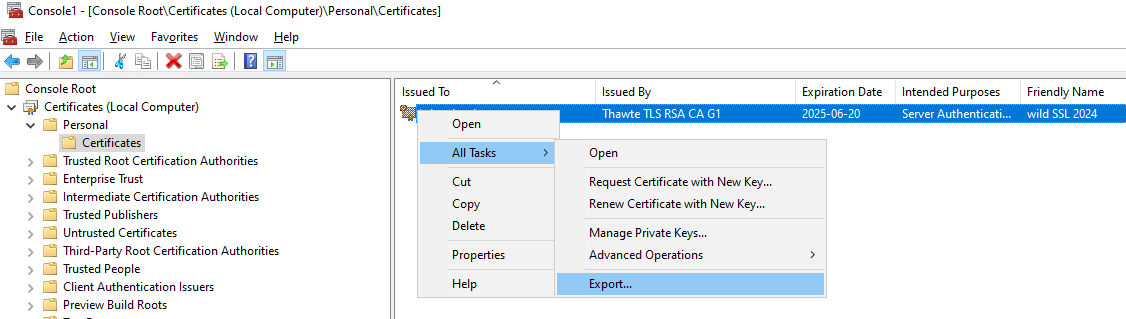
- Exported certificate as a PFX file. If you need to learn how my post on Exporting a Certificate with MMC details all the steps.
- Password for the PFX file.
The Process
- Place your PFX file in a working directory. I will be using
C:\SSLas my working directory. - Open command line. You can use Linux or Windows. The commands are all the same regardless of which OS you are using. I will be using Microsoft Windows with Windows Terminal and PowerShell.
Depending on your needs, you may need to convert your PFX file in several different ways. Here are the methods that I will cover.
- Export Certificate Only
- Export CA Certificates Only
- Export Keys Only without a Password
- Export Keys Only with a Password
- Export Everything as One File without a Password
- Export Everything as One File with a Password
All of the commands below will use the following options.
pkcs12tells OpenSSL that the file it is being fed is a PKCS#12 file. PKCS#12 is another name for a PFX file.intells OpenSSL where the source file is.outtells OpenSSL where to store the converted file.