Generate CSR with OpenSSL
There are many ways to generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request). In this post, I will show you step-by-step how to generate a CSR using OpenSSL.
Prerequisites
- OpenSSL binary installed. You can find the OpenSSL binaries on the OpenSSL wiki.
The Process
- Create a working directory.
I will be using C:\SSL as my working directory.
- Open command line. You can use Linux or Windows. The commands are all the same regardless of which OS you are using.
I will be using Microsoft Windows with Windows Terminal and PowerShell.
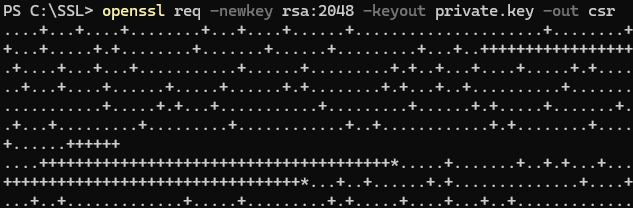
- We will use the following options to create our OpenSSL command.
reqto let OpenSSL know that we want to make a CSR.newkeyto tell Open SSL that we want a new private key.rsa:2048to tell Open SSL we want the private key encoded with RSA and 2048 bits.keyoutto tell OpenSSL where to save the private key.outto tell OpenSSL where to save the CSR.
- Using those options, we can create the OpenSSL command to generate a new private key and create the CSR. Replace PATH_TO_KEY and PATH_TO_CSR with the location where you want the private key and CSR saved.
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout PATH_TO_KEY -out PATH_TO_CSR
In my example, I will name my private key private.key, and my CSR will be named csr. The command for me will look like openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout private.key -out csr