Active Directory Recycle Bin
If you accidentally delete something in Active Directory, it can be difficult to undo. Fortunately, you can enable a recycle bin for Active Directory, making life much easier if you need to restore something.
The Active Directory Recycle Bin (sometimes called ADRB) was first introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2. You need to enable it to take advantage of it. You can never turn it off once you enable the Active Directory Recycle Bin.
Once the Active Directory Recycle Bin is enabled, when you delete an object out of Active Directory, the object is not instantly deleted. It is placed in the Active Directory Recycle Bin for some time. After some time has passed, the object is actually permanently deleted. The default retention for the recycle bin is 180 days.
In this post, I will show you step-by-step how to check the Active Directory Recycle Bin status using the GUI or PowerShell, how to enable the Active Directory Recycle Bin with the GUI or PowerShell and how to check the Active Directory Recycle Bin retention using the GUI or PowerShell.
Prerequisites
- Active Directory Forest Functional Level at Windows 2008 R2 or higher
- Active Directory Domain Functional Level at Windows 2008 R2 or higher
- Domain Admin account
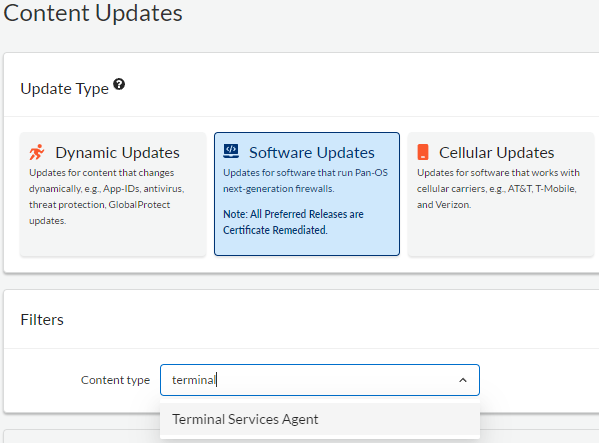
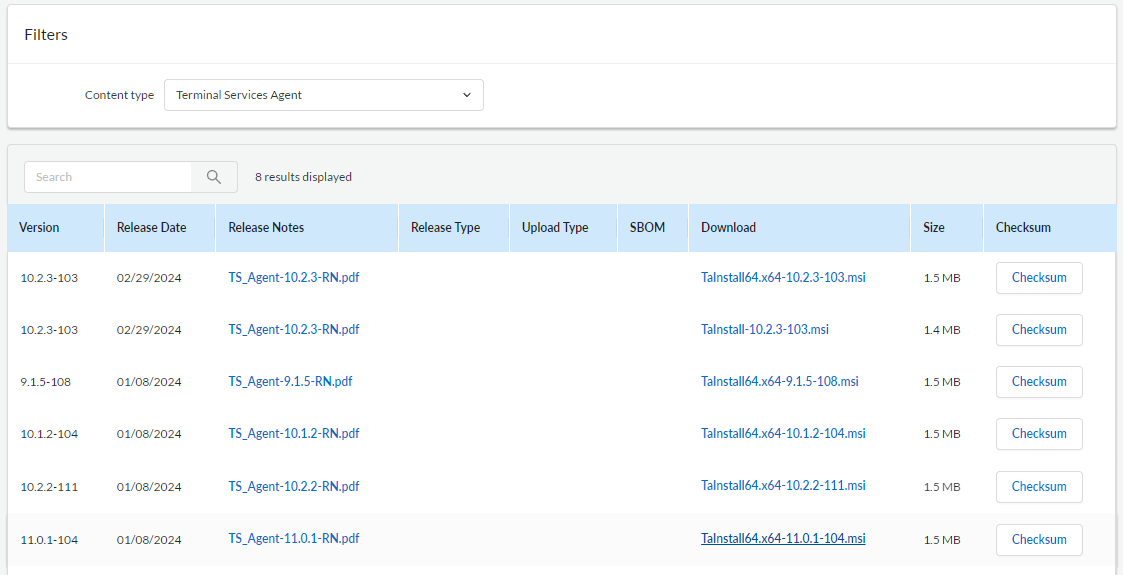
Checking Active Directory Recycle Bin Status
Before enabling the Active Directory Recycle Bin, it’s a good idea to check if it’s already enabled.
GUI Way
- Open the Active Directory Administrative Center (aka dsac)
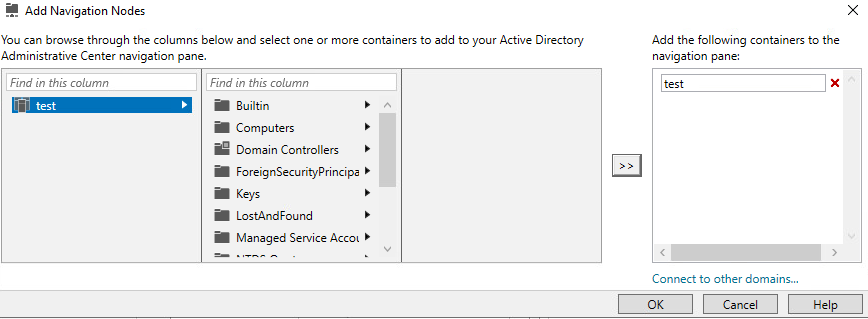
- In the top right, click on Manage > Add Navigation Nodes…
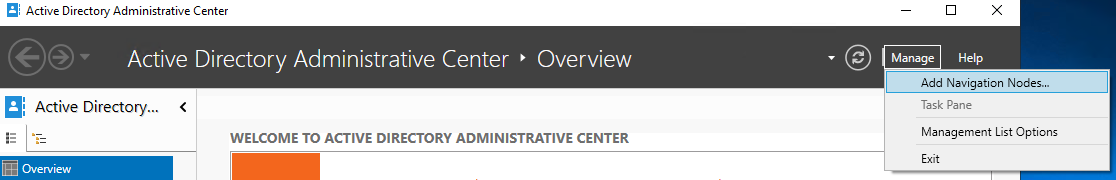
- Select your domain, click on the arrows to add it, then click ok.
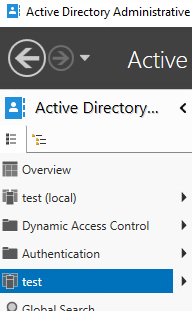
- Click on the domain.