
Palo Alto Certificate Chain Fix
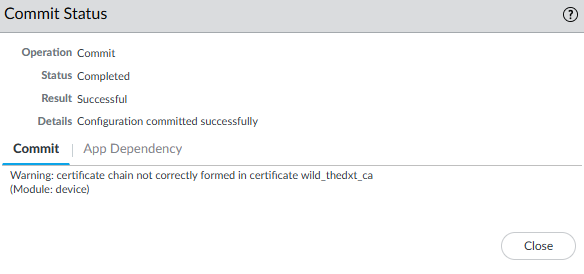
An issue I’ve run into on Palo Alto Networks firewalls is that everything seems to work when importing a certificate (usually a PFX). Until you start using the certificate, then after a validation or a commit, there’s a warning that the certificate chain is not correctly formed.
Warning: certificate chain not correctly formed in certificate wild_thedxt_ca
(Module: device)
Certificate chain issues are commonly caused when the certificate chain is out of order. You can read more about certificate chains in my blog post, Certificate Chain. If you want to read more about what can cause broken certificate chains, my blog post, Broken Certificate Chain, goes into more detail.
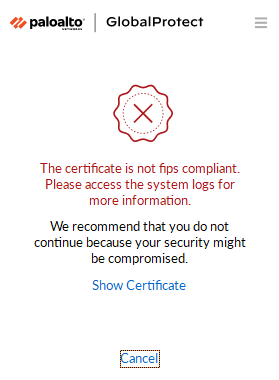
An incorrect certificate chain can cause issues with a few items on a Palo Alto firewall. One of them can be GlobalProtect when the option FULLCHAINCERTVERIFY="yes" is used during the GlobalProtect install or when the registry value named full-chain-cert-verify is set to yes in the registry path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Palo Alto Networks\GlobalProtect\Settings
In this post, I will show you step-by-step how to fix a certificate chain on a Palo Alto Networks firewall.
The Process
- Click on the Device tab.
- Click on Certificate Management > Certificates.
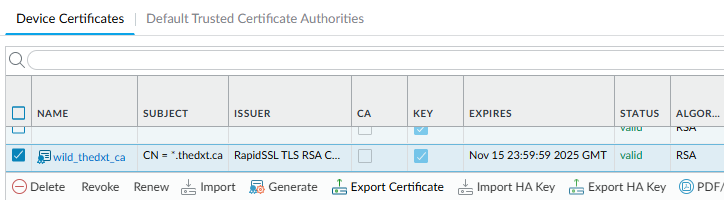
- Select the certificate that is not correctly formed and click on Export Certificate.
In my example, the certificate named wild_thedxt_ca is the one I need to fix.
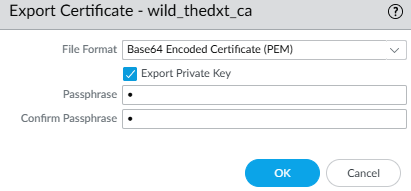
- For the File Format, select Base64 Encoded Certificate (PEM).
- Select Export Private Key and enter a Passphrase.
- Open the downloaded
pemfile with a text editor.
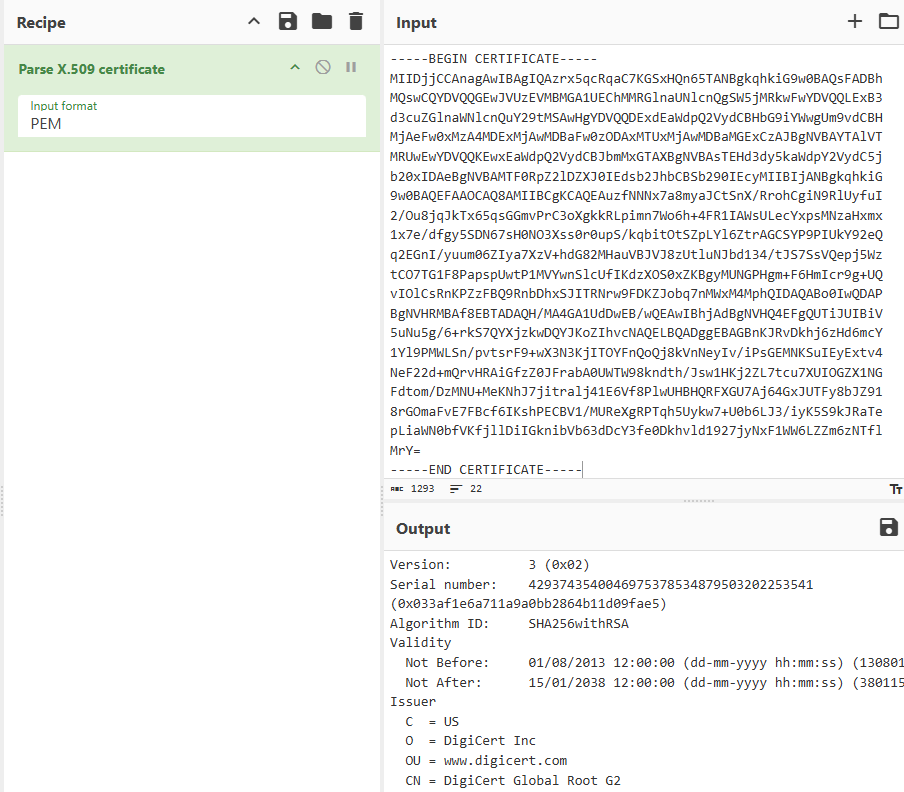
- Use something like CyberChef to decode the certificates. (Here is the recipe I used)
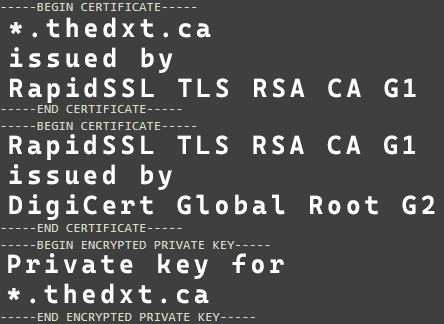
Each certificate will start with -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- and end with -----END CERTIFICATE-----
In my example, first is the wildcard certificate *.thedxt.ca issued by RapidSSL TLS RSA CA G1 (an intermediate CA). The next certificate in the chain is DigiCert Global Root G2 (a public root CA). The next certificate in the chain is RapidSSL TLS RSA CA G1 (the intermediate CA that issued my certificate).
Because each certificate doesn’t lead directly to the next certificate, the certificate chain is out of order and malformed.
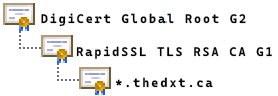
The correct certificate chain in my setup would be *.thedxt.ca issued by the intermediate CA RapidSSL TLS RSA CA G1 then the certificate for the intermediate CA RapidSSL TLS RSA CA G1 issued by the public root CA DigiCert Global Root G2. Then the public root CA certificate for DigiCert Global Root G2.
Because DigiCert Global Root G2 is a public root CA, I don’t need to include it in the PEM file, as the Palo Alto firewall already has that certificate installed (this is common for public CAs).
- Restructure your PEM file to follow the correct certificate chain order
- Your certificate
- The intermediate CA that issued your certificate
- Any other intermediate CAs until you get to the root CA.
- Your Private Key
Below is an image example of what it will look like for me.
- Save the PEM file.
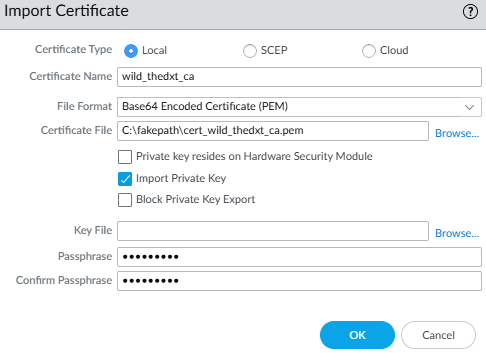
- Click on Import.
- For the Certificate Name, enter the same name as the existing malformed certificate.
- Select Import Private Key.
- Don’t select a Key File, as the private key is in the PEM file.
- Enter the passphrase you created when you exported the certificate.
- Now you can commit or validate without the certificate chain not correctly formed warning.
That’s all it takes to correct an incorrectly formatted certificate on a Palo Alto Networks firewall.
If you want to read more about fixing a certificate chain, here is the Palo Alto documentation. If you want to read more about installing a signed certificate from a public CA, here is the Palo Alto documentation.







2 thoughts on “Palo Alto Certificate Chain Fix”
What are the ramifications of seeing “untrusted issuer” in Panorama – Managed Devices – Summary – Certificate field? Is this related to this issue or merely pointing out that the issuer is not one that Palo “trusts”?
I’m not 100% sure as I haven’t played with Panorama yet. However I wonder if you have an certificate installed that is using an internal root CA and maybe that root certificate is missing on the device.